First Aid for Opioid Overdose

An opioid overdose occurs when a person takes a large amount of opioids and their body ceases to function normally, or experiences an adverse reaction.
The term “opioid” refers to a variety of natural and synthetic compounds that are regularly prescribed for pain relief.
It is important to know first aid for opioid overdoses, as casualties can cease breathing in a matter of minutes.
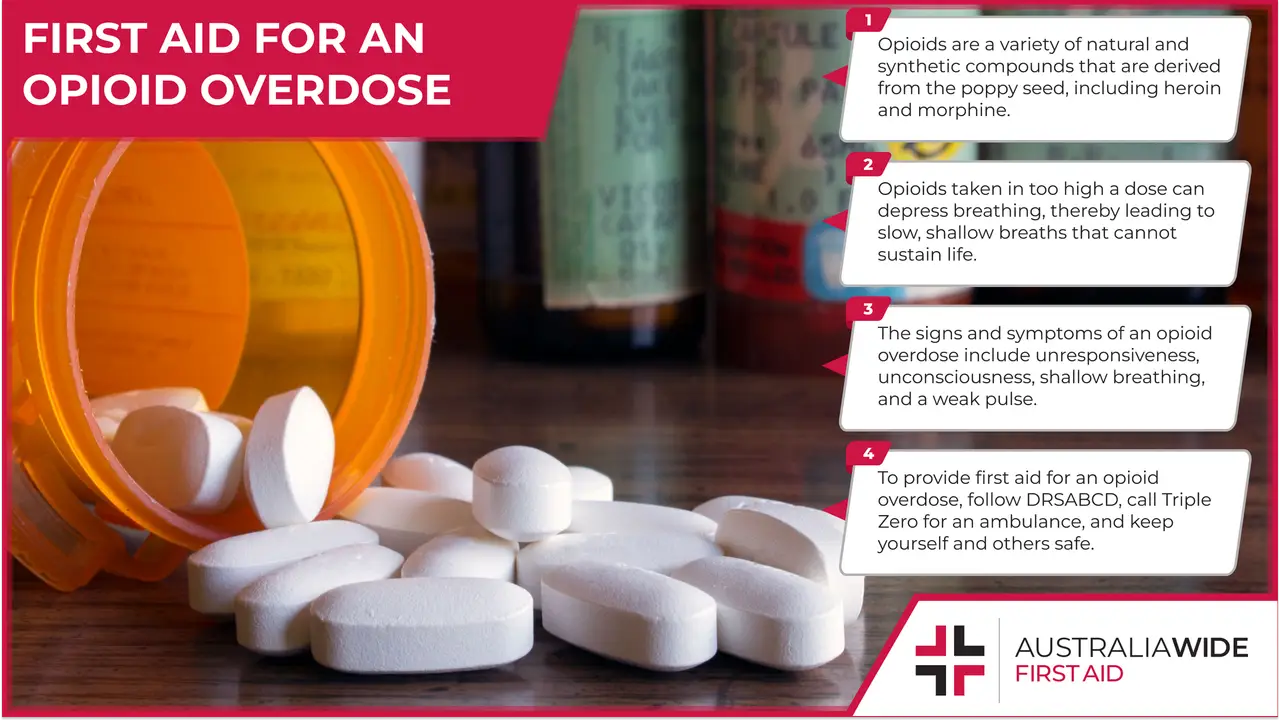
Opioids are a variety of natural and synthetic compounds that are derived from the poppy seed, including heroin, morphine, and fentanyl.
Opioids react with opioid receptors in the brain, which regulate the body’s sense of pain and reward, and so have analgesic and sedative effects.
As opioids can also cause euphoria, they are often taken for non-medicinal reasons and can lead to dependence.
People can overdose on opioids if their body is not used to it, or if they take a combination of substances at the same time.
This includes people who resume taking opioids after a period of abstinence, and whose tolerance to the drug has been reduced.
Opioids taken in too high a dose can depress breathing, thereby leading to slow, shallow breaths that cannot sustain life.
It a casualty takes opioids and begins exhibiting the following signs and symptoms, they may be experiencing an opioid overdose:
We have also a First Aid Chart that can be downloaded and printed in A2 size or smaller.
The following first aid courses look at opioid overdose:

October 13, 2023
Choking occurs when an object or a piece of food becomes lodged in the throat, blocking the airway. The adult or child will have difficulty breathing, and may lose consciousness. Quick and effective action is essential to prevent severe consequences and death.
September 22, 2023
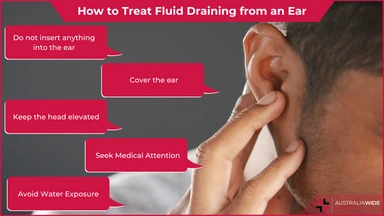
Knowing how to provide first aid for fluid draining from an ear is crucial to alleviate discomfort and potentially prevent complications.

July 31, 2023
This article covers treatment/first aid for nose bleeds, and also covers all of the common misconceptions and myths about treating a bleeding nose.